GitLab CIでClaude Codeにテストコードを生成してもらった際のtips
※アイキャッチ画像はGenSparkに作成してもらいました。
はじめに
現在クリエーションラインでは、チームでの課題として生成AIエージェント駆動の事例について取り組んでいます。または先日開催されましたLT会「[【AI駆動開発まつり】AI駆動開発 の現場テクニックを徹底紹介!(KennEjimaさん招待講演)]」で登壇を行うこととなり、何か発表できるテーマを探さねば思い試行錯誤していたところ、「生成AIによるテストコード生成」x「CICD」で面白いことできないかと思いつきました。
今回はGitLab CI x 「Calude Code」にてテストコード生成を行なった際のtipsをご紹介できればと思います。
構成
ざっくりと今回作成する成果物の構成を紹介できればと思います。
マージリクエストを作成(またはコードをリモートへPush)
│
▼
Claude Code CLI (GitLab CICD上で動作を想定)
│
▼
生成したテストコードをリモートへpush
│
▼
CICD上でGitLabのAPIを介してGitLab (リポジトリ / MR)を作成準備
成果物の対象の用意
今回は簡易的なFlaskアプリを作成して、APIの改修を行なった際にその改修箇所に対してのテストコードを生成するような状況を作りました。
<今回作成したディレクトリ構成>
.
├── Dockerfile
├── Makefile
├── README.md
├── app
│ ├── data.db
│ ├── db.py...db接続の管理周り
│ ├── main.py...Flaskアプリのエントリポイント
│ ├── requirements.txt...依存関係の管理
│ ├── routes
│ │ └── items.py...APIのルーティング設定、ビジネスロジックの記述
│ └── seed.py...DBへのシードファイル
├── docker-compose.yml...開発環境用意のDockerComposeファイル
└── tests...テストファイル格納ディレクトリClaude Code x GitLab CI/CDの設定
Claude CodeをGitLab CI/CD上で動作またMRをHTTPリクエスト介して実行させるために以下を行います
- GitLab PATの設定
- Anthropic API Keyの取得
- Claude Codeのクレジットを有効化
- GitLabの対象のリポジトリに対し環境変数を設定
- .gitlab-ci.ymlの設定
GitLab PATの設定
https://qiita.com/turupon/items/17ca6f3c770fe82ead38
上記記事を参考にKeyを取得しました。
今回リポジトリの読み書きが必要であるため「read_repository」「write_repository」を許可してください。
Anthropic API Keyの取得
https://console.anthropic.com/dashboard
上記より「Get Key」を押下しKeyを取得してください。(Claude Codeのクレジットを有効化が必要な点に注意です)
GitLabの対象のリポジトリに対し環境変数を設定
GitLab -> 対象のリポジトリ -> サイドメニューSettings -> CICDより
Variablesの項目から以下をVisibilityをMaskedを選択した上で設定してください。
GITLAB_USERNAMEANTHROPIC_API_KEYGITLAB_TOKEN(PAT)
.gitlab-ci.yml
stages:
- generate_tests
- merge_request
claude:
stage: generate_tests
image: node:24-alpine3.21
rules:
- if: '$CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == "web"'
when: always
- if: '$CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == "push" && $RUN_AI_PIPELINE == "true"'
when: always
- when: never
only:
variables:
GIT_STRATEGY: fetch
GIT_DEPTH: 0 # MRベースブランチの履歴が必要
CLAUDE_LOG: claude_output.log
before_script:
- set -e
- apk add --no-cache git curl bash python3 py3-pip
- npm install -g @anthropic-ai/claude-code
- export PATH="$PATH:$(npm bin -g)"
cache:
key: claude-global-cache
paths:
- /usr/local/lib/node_modules/
script:
- echo "Running Claude Code to generate Python tests for MR !${CI_MERGE_REQUEST_IID}"
- |
git fetch origin ${CI_MERGE_REQUEST_TARGET_BRANCH_NAME:-$CI_DEFAULT_BRANCH}
CHANGED_FILES=$(git diff --name-only origin/${CI_MERGE_REQUEST_TARGET_BRANCH_NAME:-$CI_DEFAULT_BRANCH})
echo "Changed files: $CHANGED_FILES"
if [ -z "$CHANGED_FILES" ]; then
echo "No file changes detected. Skipping Claude execution."
exit 0
fi
- |
claude \
--model claude-sonnet-4-5-20250929 \
-p "
# Context
Project: ${CI_PROJECT_PATH}
Merge Request: !${CI_MERGE_REQUEST_IID}
Target: New or modified functions in this MR
**IMPORTANT**: First read and follow the guidelines in ./Claude.md.
This file contains project-specific conventions, coding standards,
and test requirements that must be prioritized.
# Task
Generate Python unit tests for the changed code, following the
guidelines specified in ./Claude.md
# Analysis Steps
1. Review repository structure and existing test patterns
2. Analyze MR diff to identify changed/added functions
3. Separate concerns:
- Use full repo context to understand architecture and patterns
- Use diff to identify specific changes requiring tests
4. This separation ensures tests accurately reflect intended behavior
# Requirements
1. Framework: Use pytest conventions (or as specified in Claude.md)
2. Location: Place tests in 'tests/unit/' directory (or as specified in Claude.md)
3. Coverage: At least one test case per public function/class
4. Constraint: Avoid changing production code unless strictly necessary for testability
# Critical Constraints - NO MOCKING
- **NEVER use mocks, patches, monkeypatch, or stubs**
- Test against real implementations only
- This ensures implementation actually exists and prevents false positives
- If dependencies are complex, create minimal real test fixtures
- This eliminates the need for mock verification in code reviews
# Validation Process
After generating each test file:
1. Execute the generated tests using pytest
2. Verify all tests pass successfully
3. If any test fails or is flaky:
- Analyze the root cause
- Fix the test code
- Re-run until stable
4. Report any execution errors or unstable tests detected
5. This automation catches issues before human review
# Output
- pytest-formatted test files adhering to Claude.md guidelines
- Comprehensive test coverage for all public APIs
- All tests verified to execute successfully
- Summary of any issues detected and resolved during validation
"\
--permission-mode acceptEdits \
--allowedTools 'Read(*) Write(*) Edit(*) mcp__gitlab' \
--debug | tee $CLAUDE_LOG
artifacts:
paths:
- tests/
- $CLAUDE_LOG
expire_in: 24 hour
create_mr:
stage: merge_request
image: alpine:latest
needs:
- job: claude
artifacts: true
dependencies:
- claude
rules:
- if: '$CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == "web"'
when: always
- if: '$CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == "push" && $RUN_AI_PIPELINE == "true"'
when: always
- when: never
before_script:
- set -e
- apk add --no-cache git curl bash
- git config --global user.email "ci-bot@creationline.com"
- git config --global user.name "GitLab CI Bot"
script:
- export TARGET_BRANCH="${CI_MERGE_REQUEST_TARGET_BRANCH_NAME:-$CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME}"
- export BRANCH_NAME="ai/generated-tests-${CI_MERGE_REQUEST_IID}-$(date +%Y%m%d-%H%M%S)"
- git fetch origin $TARGET_BRANCH
- git checkout -b ${BRANCH_NAME} origin/$TARGET_BRANCH
- git add tests/ || true
- if git diff --cached --quiet; then
echo "No new test files to commit. Skipping MR creation.";
exit 0;
fi
- git commit -m "Add AI-generated tests for MR !${CI_MERGE_REQUEST_IID}" || echo "No changes to commit"
- git push -f https://gitlab-ci-token:${CI_JOB_TOKEN}@${CI_SERVER_HOST}/${CI_PROJECT_PATH}.git ${BRANCH_NAME}
- |
echo "Creating MR from ${BRANCH_NAME} -> ${TARGET_BRANCH}"
curl --fail --request POST \
--header "PRIVATE-TOKEN: ${GITLAB_TOKEN}" \
"${CI_API_V4_URL}/projects/${CI_PROJECT_ID}/merge_requests" \
--form "source_branch=${BRANCH_NAME}" \
--form "target_branch=${TARGET_BRANCH}" \
--form "title=Add AI-generated tests for MR !${CI_MERGE_REQUEST_IID}" \
--form "description=This MR was automatically generated by Claude Code for !${CI_MERGE_REQUEST_IID}." \
--form "labels=auto-generated,testing"
artifacts:
when: always
expire_in: 24 hours
rulesによるCI実行条件の厳格化やgit fetch..にてターゲットブランチへの差分のみをプロンプトに渡すなどの処理をしています。
工夫点
今回構築を行うにあたって工夫した点があるため、紹介します。
https://www.anthropic.com/engineering/claude-code-best-practices
上記リンクにあるようにClaude Codeにはいくつかのベストプラクティスが存在し、テストコード生成に関するものも存在しました。そちらのプラクティスをいくつか踏襲するためCI上で工夫した箇所があるため、そちらも併せて紹介できればと思います。
コンテキストの分離
今回の構成ではClaude Codeにプロンプトを渡す際にリポジトリの情報はマークダウンファイルとして、テスト対象のコードはgit fetch...にて差分を抽出してコードベースで渡しています。
<ポジトリの情報のマークダウンファイルを明示的に読み込ませる>
**IMPORTANT**: First read and follow the guidelines in ./Claude.md.
This file contains project-specific conventions, coding standards,
and test requirements that must be prioritized.
<git fetch...にて差分を抽出する>
- |
git fetch origin ${CI_MERGE_REQUEST_TARGET_BRANCH_NAME:-$CI_DEFAULT_BRANCH}
CHANGED_FILES=$(git diff --name-only origin/${CI_MERGE_REQUEST_TARGET_BRANCH_NAME:-$CI_DEFAULT_BRANCH})
echo "📄 Changed files: $CHANGED_FILES"
if [ -z "$CHANGED_FILES" ]; then
echo "No file changes detected. Skipping Claude execution."
exit 0
fi
上記を設定することで重要情報の識別性が上がり、Calude Codeが迷いにくくなるほか指示が明確になりテスト生成の精度の向上が期待できます。
Mock作成の禁止
Mockを作成させることは基本的にアンチパターンとされています。
理由としては、実装自体は存在しないのにテストコードのみが出来上がる問題があり、それを避けるためです。今回は以下のように設定しました。
# Critical Constraints - NO MOCKING
- **NEVER use mocks, patches, monkeypatch, or stubs**
- Test against real implementations only
- This ensures implementation actually exists and prevents false positives
- If dependencies are complex, create minimal real test fixtures
- This eliminates the need for mock verification in code reviewsClaude Code自身にテストを実行させる
Claude Code公式には以下のような記述があります。
クロードにテストに合格するコードを書くように指示し、テストを変更しないように指示します。すべてのテストに合格するまで続けるようにクロードに伝えます。
After generating each test file: 1. Execute the generated tests using pytest 2. Verify all tests pass successfully 3. If any test fails or is flaky: - Analyze the root cause - Fix the test code - Re-run until stable 4. Report any execution errors or unstable tests detected 5. This automation catches issues before human review
実際に動作させてみる
実際に変更をリモートへPushし(今回は簡単なCRUDアプリのDeleteメソッド)マージリクエストを作成しCIを実行してみました。
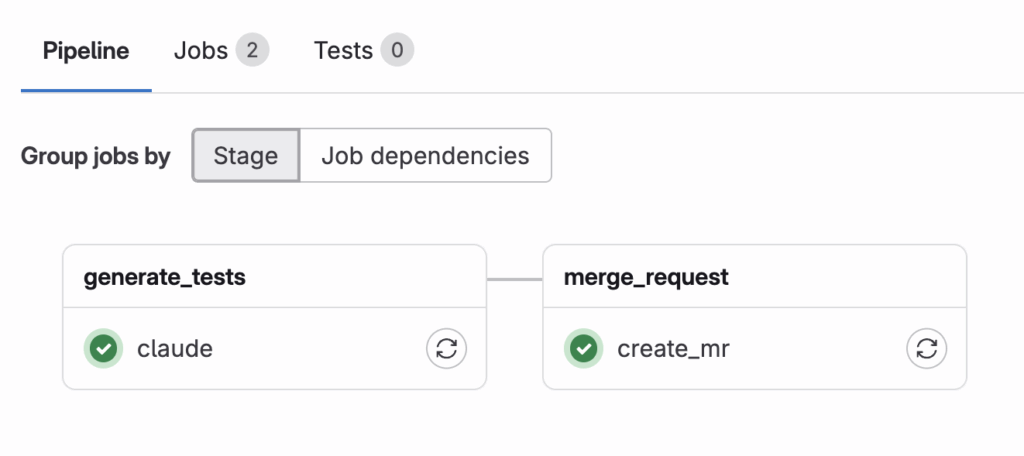
うまく実行できたようです。生成されたものを見てみましょう
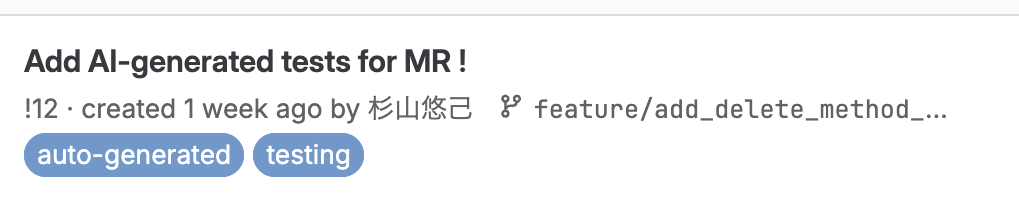
作成されたMRから、、、
import pytest
import sys
from pathlib import Path
import psycopg2
import os
# Add app directory to path for imports
app_dir = Path(__file__).parent.parent.parent / "app"
sys.path.insert(0, str(app_dir))
import db
class TestGetConnection:
"""Test cases for get_connection function."""
def test_get_connection_success(self):
"""Test successful database connection."""
conn = db.get_connection()
assert conn is not None
assert isinstance(conn, psycopg2.extensions.connection)
assert conn.closed == 0 # Connection is open
conn.close()
def test_get_connection_can_execute_query(self):
"""Test that connection can execute a simple query."""
conn = db.get_connection()
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute("SELECT 1")
result = cur.fetchone()
assert result == (1,)
cur.close()
conn.close()
class TestInitDb:
"""Test cases for init_db function."""
def test_init_db_creates_table(self):
"""Test that init_db creates the items table successfully."""
# Drop table if it exists
conn = db.get_connection()
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS items")
conn.commit()
cur.close()
conn.close()
# Initialize database
db.init_db()
# Verify table exists
conn = db.get_connection()
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute("""
SELECT EXISTS (
SELECT FROM information_schema.tables
WHERE table_name = 'items'
)
""")
table_exists = cur.fetchone()[0]
cur.close()
conn.close()
assert table_exists is True
def test_init_db_table_structure(self):
"""Test that items table has correct structure."""
# Ensure table exists
db.init_db()
# Check table structure
conn = db.get_connection()
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute("""
SELECT column_name, data_type, is_nullable
FROM information_schema.columns
WHERE table_name = 'items'
ORDER BY ordinal_position
""")
columns = cur.fetchall()
cur.close()
conn.close()
# Verify columns
assert len(columns) == 2
assert columns[0][0] == 'id'
assert columns[1][0] == 'name'
assert columns[1][2] == 'NO' # name is NOT NULL
class TestInsertItem:
"""Test cases for insert_item function."""
def setup_method(self):
"""Setup test database before each test."""
db.init_db()
# Clean up any existing items
conn = db.get_connection()
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute("DELETE FROM items")
conn.commit()
cur.close()
conn.close()
def test_insert_item_success(self):
"""Test successful item insertion."""
db.insert_item("Test Item")
# Verify item was inserted
conn = db.get_connection()
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute("SELECT name FROM items WHERE name = %s", ("Test Item",))
result = cur.fetchone()
cur.close()
conn.close()
assert result is not None
assert result[0] == "Test Item"
def test_insert_item_with_special_characters(self):
"""Test item insertion with special characters."""
special_name = "Item's \"special\" name & symbols"
db.insert_item(special_name)
# Verify item was inserted
conn = db.get_connection()
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute("SELECT name FROM items WHERE name = %s", (special_name,))
result = cur.fetchone()
cur.close()
conn.close()
assert result is not None
assert result[0] == special_name
def test_insert_item_with_japanese_characters(self):
"""Test item insertion with Japanese characters."""
japanese_name = "日本語アイテム"
db.insert_item(japanese_name)
# Verify item was inserted
conn = db.get_connection()
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute("SELECT name FROM items WHERE name = %s", (japanese_name,))
result = cur.fetchone()
cur.close()
conn.close()
assert result is not None
assert result[0] == japanese_name
~省略~
class TestDeleteItem:
"""Test cases for delete_item function."""
def setup_method(self):
"""Setup test database before each test."""
db.init_db()
# Clean up any existing items
conn = db.get_connection()
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute("DELETE FROM items")
conn.commit()
cur.close()
conn.close()
def test_delete_item_success(self):
"""Test successful item deletion."""
db.insert_item("Item to Delete")
items = db.get_all_items()
item_id = items[0]["id"]
result = db.delete_item(item_id)
assert result == 1
# Verify item was deleted
remaining_items = db.get_all_items()
assert len(remaining_items) == 0
def test_delete_item_not_found(self):
"""Test delete_item returns 0 when item doesn't exist."""
result = db.delete_item(999999)
assert result == 0
def test_delete_item_leaves_other_items(self):
"""Test that deleting one item doesn't affect others."""
db.insert_item("Item 1")
db.insert_item("Item 2")
db.insert_item("Item 3")
items = db.get_all_items()
middle_item_id = items[1]["id"]
result = db.delete_item(middle_item_id)
assert result == 1
# Verify only the specified item was deleted
remaining_items = db.get_all_items()
assert len(remaining_items) == 2
assert remaining_items[0]["name"] == "Item 1"
assert remaining_items[1]["name"] == "Item 3"
ちゃんと差分を抽出したところだけのテストコードが作成できています。
指定した通りMockも使っていないですね。
終わりに
生成AIとCIを組み合わせて何か実装したいなとは前々から考えていたため、今回それを形にすることができてよかったです。
あまりテストコードを生成AIに作ってもらう経験がなかったのですが、何も考えずにそのまま実装してしまうのはかなり危険であると感じました。
Calude Codeの「親切心」でモックで実装がないのにテストコードだけ作ってしまうというのは、実際に動作や調査をしていないと分からなかった情報であり、大変勉強になりました。
今回はテストコードという観点で生成AIを利用しましたがきっとユースケースごとにプラクティスやアンチパターンが存在すると思うので、調査しながら利用していけたらと思います。
また今後さらにチャレンジしたいこととしてテスト実行の自動化(MPC用いたもの)など行っていきたいと思っています。成果が出たら記事にしたいと思います。





